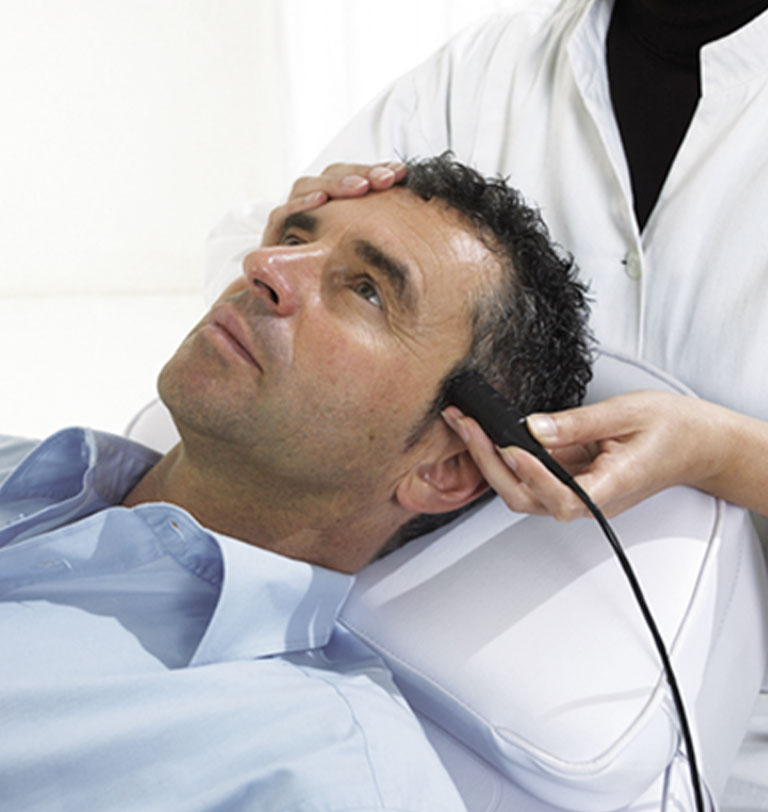
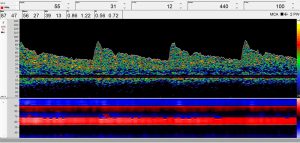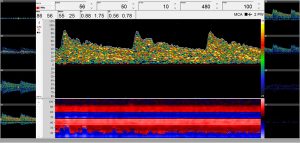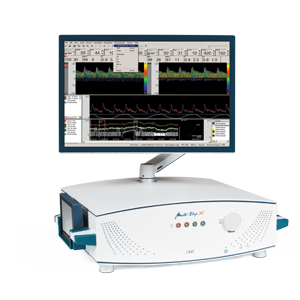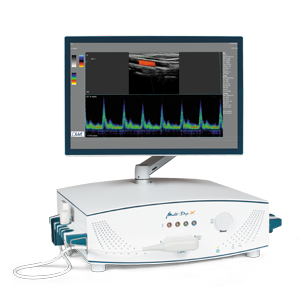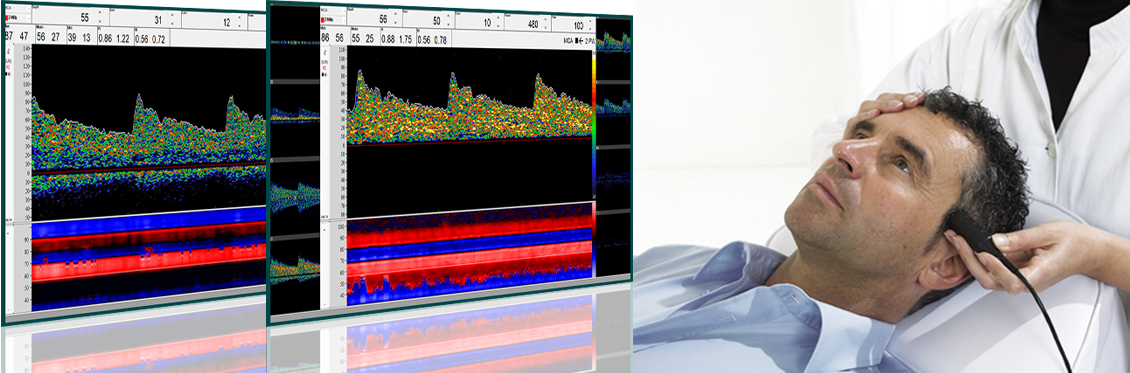

As a non-invasive examination method, the “Routine Doppler” is primarily used to diagnose transcranial, extracranial and peripheral vascular diseases. It is also receiving increased attention for invasive surgical measures. In this process, the user notably obtains valuable information about blood flow velocity and any changes thereto, vascular resistance, the peak systolic velocity, the direction of blood flow and significant differences between both sides. This allows safe and fast detection of the finest vessels even in the case of neurosurgical operations.
Applications of the routine diagnostics include:
Examination of cerebrovascular disorders
With 1 and 2 MHz handheld probes
- Cerebrovascular occlusive diseases
- Circulatory disorders in the brain (TIA)
- Brain death diagnostics
- Subarachnoid haemorrhages
- Vasospasms
- Traumatic brain injury
- Stroke diagnostics
- Cerebral microangiopathy
- Sickle cell diagnostics
Examinations of diseases of the extracranial and peripheral vascular systems
With 4 and 8 MHz handheld probes
- Diffuse and well-defined arteriopathies
- Arteriosclerosis
- Advanced stenoses and arterial occlusions
- Arterial and venous stents
Intraoperative examinations
With 16 MHz microprobes
- Microvascular anastomoses
- Extracranial-intracranial bypass
- Bypassing large aneurysms
- Aneurysm clipping
- Intraoperative monitoring (microvascular Doppler)
- Identifying afferent and efferent vessels
- Stereotactic biopsy
- Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas